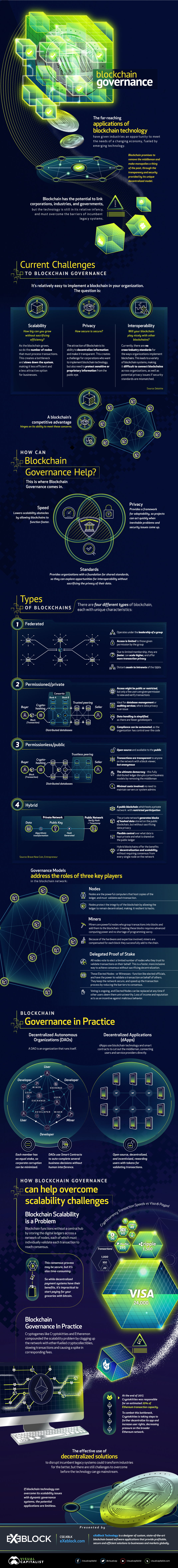
Blockchain Governance: How Boundaries Can Help the Blockchain to Scale
By – Published in on September 26, 2018

The blockchain offers a long overdue upgrade for our changing economy.
However, the world isn’t quite ready for broadscale blockchain adoption. The technology is still in its relative infancy, and to reach its true potential the blockchain must be able to successfully replace existing systems while also operating at meaningful scale.
Today’s infographic comes to us from eXeBlock Technology, and it explores how good blockchain governance can help solve the pressing challenges around blockchain adoption and implementation, including the ever-present issue of scalability.
SO YOU SAY YOU WANT A BLOCKCHAIN
While it’s relatively easy to implement a blockchain in an organization, it’s far more difficult to decide just how that network should operate. For a blockchain to generate and hold any real competitive advantage, there are a few key questions to consider:
Scalability
How big can you grow before sacrificing efficiency? As the blockchain grows, so do the number of nodes to process transactions. This creates a bottleneck and slows down the system.
Privacy
What are your privacy needs? The attraction of the blockchain lies in its ability to decentralize information and make it transparent, but this creates a challenge for corporations who use the blockchain to handle sensitive or proprietary information.
Interoperability
Will your blockchain play nicely with other blockchains? There are a number of blockchain configurations – and to date, no cross-industry standards. This means your blockchain might not collaborate smoothly with another blockchain, particularly if the security standards are mismatched.
HOW CAN BLOCKCHAIN GOVERNANCE HELP?
Blockchain governance is concerned with solving these problems by:
Reducing scalability obstacles by finding ways for blockchains to reach consensus faster without sacrificing decentralization
Providing a foundation for shared standards, so organizations can collaborate without risking the privacy of their data
Providing a framework for adaptability – a playbook for the blockchain to rely on when inevitable problems and security issues crop up
Think of governance as a constitution to help the blockchain run smoothly: it improves efficiency, encourages collaboration, and outlines a course of action when the system falters.
TYPES OF BLOCKCHAINS
There are four different types of blockchains, each with unique characteristics:
Federated
Operates under the leadership of a group, and access is limited to only members of the group
Due to limited membership, they are faster, can scale higher, and offer more transaction privacy
Permissioned/private
Access might be public or restricted, but only a few users are given permission to view and verify transactions
Ideal for database management or auditing services, where data privacy is an issue
Compliance can be automated, as the organization has control over the code
Permissionless/public
Open-source and available to the public
Transactions are transparent to anyone on the network with a block viewer, but anonymous.
The ultimate democracy – this fully distributed ledger disrupts current business models by removing the middleman
Minimal costs involved: no need to maintain servers or system admins
Hybrid
A public blockchain, which hosts a private network with restricted participation
The private network generates blocks of hashed data stored on the public blockchain, but without sacrificing data privacy
Flexible control over what data is kept private and what is shared on the public ledger
Hybrid blockchains offer the benefits of decentralisation and scalability, without requiring consensus from every single node on the network
Within each of these systems, blockchain governance outlines different standards for privacy and security. Governance determines how consensus is reached, and how many nodes are required. It establishes who has access to what information, and how that data is encrypted. Governance sets up the foundations for blockchains to scale according to the needs of the organization.
Blockchain governance exists to smooth the transition to widespread adoption, providing organizations with dynamic solutions to make their blockchain suit their needs without sacrificing the security of decentralization.
For more amazing infographics visit www.visualcapitalist.com.

Comments